DDS-SECURITY 拓展规范为 DDS 引入了安全机制。这些机制包括了认证、访问控制、加密、操作日志和数据标签。
基础架构
security 机制由下面几个部分构成:
Authentication:用于身份验证和密钥协商。协商结果为生成一个用于 crypto 插件使用的密钥。
Access Control:访问控制。
Cryptographic:数据加密。
Security 新增了两个新的 Qos,分别是 Property 和 DataTag,其定义如下:
@extensibility(APPENDABLE)
struct Property_t {
string name;
string value;
@non_serialized
boolean propagate; (1)
};当且仅当 propagate 的值为 true 时才会在序列化的时候序列化此值。
property 实际上是用来传递 security 配置信息的,相当于一个 map。
@extensibility(APPENDABLE)
struct BinaryProperty_t {
string name;
OctetSeq value;
@non_serialized boolean propagate;
};Token 是一个拓展的 Qos,其构成如下:
@extensibility(APPENDABLE)
struct DataHolder { (1)
string class_id;
PropertySeq properties;
BinaryPropertySeq binary_properties;
};security 中的所有 Token 都是此结构的别名
拓展的发现机制
安全机制对内置的 Discovery 进行了拓展,以支持安全机制,这些拓展后的内容分别是:
@extensibility(MUTABLE)
struct ParticipantBuiltinTopicData: DDS::ParticipantBuiltinTopicData {
@id(0x1001) IdentityToken identity_token;
@id(0x1002) PermissionsToken permissions_token;
@id(0x1005) ParticipantSecurityInfo security_info;
};@extensibility(MUTABLE)
struct PublicationBuiltinTopicData: DDS::PublicationBuiltinTopicData {
@id(0x1004) EndpointSecurityInfo security_info;
};@extensibility(MUTABLE)
struct SubscriptionBuiltinTopicData: DDS::SubscriptionBuiltinTopicData {
@id(0x1004) EndpointSecurityInfo security_info;
};这些拓展后的 BuiltinData 用来在 DDS 之间传递 security 相关的信息。
除此之外,为了进一步增强安全机制,security 还引入和新的 Builtin Entities:
Builtin Entities
除了 RTPS Discovery 中的 Builtin Entities 外,security 还引入的新的 Topic 用来保护 Topic 信息:
| 下面被拓展的数据类型都来自 拓展的发现机制 而不是 RTPS 规范中定义的数据类型。 |
DCPSParticipantsSecure [1]
@extensibility(MUTABLE)
struct ParticipantBuiltinTopicDataSecure: ParticipantBuiltinTopicData {
@id(0x1006) @optional IdentityStatusToken identity_status_token;
};和 SPDP 不同,DCPSParticipantsSecu 使用 Reliable 的 DataReader/DataWriter.
RW 的 EntityID 分别为:
SPDPbuiltinParticipantsSecureReader
SPDPbuiltinParticipantsSecureWriter
认证完成后,任何来着已被认证的 participant 的 ParticipantBuiltinTopicData 消息都会被忽略,应当使用 ParticipantBuiltinTopicDataSecure
DCPSPublicationsSecure [2]
@extensibility(MUTABLE)
struct PublicationBuiltinTopicDataSecure: PublicationBuiltinTopicData {
@id(0x1003) DataTags data_tags;
};RW 的 EntityID 分别为:
SEDPbuiltinPublicationsSecureWriter
SEDPbuiltinPublicationsSecureReader
如果 Topic 被 AccessControl 认为不是敏感的,则通过 DCPSPublications Topic 传输,否则使用 DCPSPublicationsSecure 传输。
DCPSSubscriptionsSecure [3]
@extensibility(MUTABLE)
struct SubscriptionBuiltinTopicDataSecure: SubscriptionBuiltinTopicData {
@id(0x1003) DataTags data_tags;
};RW 的 EntityID 分别为:
SEDPbuiltinSubscriptionsSecureWriter
SEDPbuiltinSubscriptionsSecureReader
如果 Topic 被 AccessControl 认为不是敏感的,则通过 DCPSSubscriptions Topic 传输,否则使用 DCPSSubscriptionsSecure 传输。
DCPSParticipantMessageSecure
DCPSParticipantMessageSecure 用于 WLP。
DCPSParticipantStatelessMessage [4]
由于现有的内置 Topic 无法用于交换认证信息,因此引入了 DCPSParticipantStatelessMessage 用于此目的。
为了防止序列号攻击,此 Topic 使用 Best-Effort DataReader/DataWriter。
RW 的 EntityID 分别为:
BuiltinParticipantStatelessMessageWriter
BuiltinParticipantStatelessMessageReader
typedef octet[16] GUID_t;
@extensibility(APPENDABLE)
struct MessageIdentity {
GUID_t source_guid;
long long sequence_number;
};
typedef string<> GenericMessageClassId;
@extensibility(APPENDABLE)
struct ParticipantGenericMessage {
/* target for the request. Can be GUID_UNKNOWN */
MessageIdentity message_identity;
MessageIdentity related_message_identity;
GUID_t destination_participant_guid;
GUID_t destination_endpoint_guid;
GUID_t source_endpoint_guid;
GenericMessageClassId message_class_id;
DataHolderSeq message_data;
};
typedef ParticipantStatelessMessage ParticipantGenericMessage;数据格式
不同的 GenericMessageClassId 储存在 message_data 中的数据也不同。
| GenericMessageClassId | 值 |
|---|---|
GMCLASSID_SECURITY_AUTH_HANDSHAKE | 只包含 HandshakeMessageToken |
GMCLASSID_SECURITY_AUTH_REQUEST | 只包含 AuthRequestMessageToken |
DCPSParticipantVolatileMessageSecure [5]
此 Topic 用于在 DomainParticipant 之间交换密钥。此 RW 是 Reliable 的,且 Durability Qos 被设置为 VOLATILE。
RW 的 EntityID 分别为:
BuiltinParticipantVolatileMessageSecureWriter
BuiltinParticipantVolatileMessageSecureReader
| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
is_read_protected | false |
is_write_protected | false |
is_discovery_protected | false |
is_liveliness_protected | false |
| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
is_read_protected | false |
is_write_protected | false |
is_discovery_protected | false |
is_liveliness_protected | false |
is_submessage_protected | true |
is_payload_protected | false |
is_key_protected | false |
Qos 相关的设置如下:
| Policy | Value |
|---|---|
RELIABILITY | kind= RELIABLE |
HISTORY | kind= KEEP_ALL |
DURABILITY | kind= VOLATILE |
| Policy | Value |
|---|---|
RELIABILITY | kind= RELIABLE |
HISTORY | kind= KEEP_ALL |
DURABILITY | kind= VOLATILE |
数据格式
| GenericMessageClassId | 值 |
|---|---|
GMCLASS_SECURITY_PARTICIPANT_CRYPTO_TOKENS | ParticipantCryptoTokenSeq |
GMCLASSID_SECURITY_DATAWRITER_CRYPTO_TOKENS | DatawriterCryptoTokenSeq |
GMCLASSID_SECURITY_DATAREADER_CRYPTO_TOKENS | DatareaderCryptoTokenSeq |
身份认证
身份认证内置插件为 PKIDH。其中 PKI 是公共密钥基础设施,通过证书验证对方身份,DH 是密钥协商算法,用来协商出可供 crypto 插件使用的密钥。
对比 SSL 协议,DDS 的认证协议具备以下特点:
双向认证:SSL 只需要客户端验证服务器的证书,而 DDS 双方都需要验证对方的证书。
双重角色:SSL 具备明确的客户端和服务器角色。而 DDS 在认证的第一步依赖 GUID 的字典序判断自己的角色。其中 GUID 较小者充当客户端的角色,负责发起认证请求。
配置
PKIDH 的体系中,一般需要服务器配置 cert,客户端配置 store 和 cert 用于认证,同时双方配置私钥用以数字签名和加密操作。而 DDS security 的体系中,由于是双向认证,因此双方都需要配置 store。双方的配置相同,均为:
| 属性名 | 值 |
|---|---|
dds.sec.auth.identity_ca | CA 证书。用来验证对方证书的有效性。 |
dds.sec.auth.private_key | 自己的私钥。用来在认证过程中进行数字签名 |
dds.sec.auth.identity_certificate | 自己的证书 |
| 除此之外,若 private_key 还设有密码。还需要添加 dds.sec.auth.password |
认证协议
认证由 SPDP 触发,当 SPDP 发现新的 participant 后调用安全插件,从而进入认证过程。认证过程中 GUID 较小者(字典顺序)为客户端,较大者作为服务器。下面是两者的握手过程:
服务器和客户端双方都配置了 CA 证书,用来验证对方证书的有效性。双方用于交换的整数 C1, C2 都被 CA 进行了签名。下面是对三个步骤的详细解释:
客户端生成用于交换信息的公钥 DH1,然后将
(C1, Hash(C1), Change1, DH1)发送给服务器。服务器使用本地 CA 验证 C1,然后生成公钥 DH2,然后将
(C2, Hash(C2), Change1, Change2, DH2, Hash(c1), DH1, Sign)发送给客户端。客户端验证证书 C2,根据 DH2 和 DH 私钥计算出对称密钥。然后发送
(Hash(C1), Hash(C2), DH1, DH2, Change1, Change2, Sign)到服务器。服务器根据 DH1 和用于 DH2 的私钥计算出对称密钥。
Details
下面简要叙述了根据公钥和密钥计算共享密钥的方法(以椭圆曲线为例):
双方各自在椭圆曲线 E 和此曲线上一点 G 为基础,再选取一个大素数 N。这些参数都是公开的。
A 使用私钥计算出 A = privK1 * G1 得到公钥 A。
B 使用私钥计算出 B = privk2 * G2 得到公钥 B。
A, B 交换公钥。
A 使用 B 和 privK1 计算共享密钥 Ka。B 使用 A 和 privk2 计算 Kb。
由于椭圆曲线上的乘法满足交换律(即 A * B = B * A),因此 Ka == Kb。
对应到 PKIDH 的方法中,上述三个步骤分别对应了:
begin_handshake_request 创建 HandshakeRequestMessageToken。
begin_handshake_reply 接受 HandshakeRequestMessageToken 并发送 HandshakeReplyMessageToken。
begin_handshake_request → process_handshake 接受 HandshakeReplyMessageToken 并完成 Client 握手。
begin_handshake_reply → process_handshake 接受 HandshakeFinalMessageToken 并完成 Server 握手。
认证过程中的数据结构
假设认证过程为 SPDP + Auth + SEDP,下面叙述了涉及到的数据结构:
IdentityToken:通过 SPDP 发送消息,用来通知对方配置算法。
HandshakeRequestMessageToken: 客户端通过 StatelessWriter 发送的认证请求。
HandshakeReplyMessageToken: 服务端通过 StatelessWriter 发送的认证响应。
HandshakeFinalMessageToken: 客户端通过 StatelessWriter 发送的最后一次握手信息。
IdentityHandle: 透明数据类型,用来存储本地配置的证书、算法等。
HandshakeHandle: 透明数据类型,用来存储握手过程中设计的数据。
通过上面的数据结构,双方能够进行算法协商和认证握手过程。
访问控制
访问控制插件由两个文件进行配置:
Domain Governance Document:定义了 domain 的加密方式。
DomainParticipant permissions document:定义了 domain 的权限信息。
Details
Domain Governance Document 的 XSD 定义如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" elementFormDefault="qualified"
attributeFormDefault="unqualified">
<xs:element name="dds" type="DomainAccessRulesNode" />
<xs:complexType name="DomainAccessRulesNode">
<xs:sequence minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1">
<xs:element name="domain_access_rules" type="DomainAccessRules" />
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="DomainAccessRules">
<xs:sequence minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element name="domain_rule" type="DomainRule" />
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="DomainRule">
<xs:sequence minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1">
<xs:element name="domains" type="DomainIdSet" />
<xs:element name="allow_unauthenticated_participants" type="xs:boolean" />
<xs:element name="enable_join_access_control" type="xs:boolean" />
<xs:element name="discovery_protection_kind" type="ProtectionKind" />
<xs:element name="liveliness_protection_kind" type="ProtectionKind" />
<xs:element name="rtps_protection_kind" type="ProtectionKind" />
<xs:element name="topic_access_rules" type="TopicAccessRules" />
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="DomainIdSet">
<xs:choice minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element name="id" type="DomainId" />
<xs:element name="id_range" type="DomainIdRange" />
</xs:choice>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:simpleType name="DomainId">
<xs:restriction base="xs:nonNegativeInteger" />
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:complexType name="DomainIdRange">
<xs:choice>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="min" type="DomainId" />
<xs:element name="max" type="DomainId" minOccurs="0" />
</xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="max" type="DomainId" />
</xs:choice>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:simpleType name="ProtectionKind">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:enumeration value="ENCRYPT_WITH_ORIGIN_AUTHENTICATION" />
<xs:enumeration value="SIGN_WITH_ORIGIN_AUTHENTICATION" />
<xs:enumeration value="ENCRYPT" />
<xs:enumeration value="SIGN" />
<xs:enumeration value="NONE" />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="BasicProtectionKind">
<xs:restriction base="ProtectionKind">
<xs:enumeration value="ENCRYPT" />
<xs:enumeration value="SIGN" />
<xs:enumeration value="NONE" />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:complexType name="TopicAccessRules">
<xs:sequence minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element name="topic_rule" type="TopicRule" />
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="TopicRule">
<xs:sequence minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1">
<xs:element name="topic_expression" type="TopicExpression" />
<xs:element name="enable_discovery_protection" type="xs:boolean" />
<xs:element name="enable_liveliness_protection" type="xs:boolean" />
<xs:element name="enable_read_access_control" type="xs:boolean" />
<xs:element name="enable_write_access_control" type="xs:boolean" />
<xs:element name="metadata_protection_kind" type="ProtectionKind" />
<!-- DDSSEC11-11 -->
<xs:element name="data_protection_kind" type="BasicProtectionKind" />
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:simpleType name="TopicExpression">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string" />
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:schema>DomainParticipant permissions document 的 xsd 定义如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" elementFormDefault="qualified"
attributeFormDefault="unqualified">
<xs:element name="dds" type="PermissionsNode" />
<xs:complexType name="PermissionsNode">
<xs:sequence minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1">
<xs:element name="permissions" type="Permissions" />
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="Permissions">
<xs:sequence minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element name="grant" type="Grant" />
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="Grant">
<xs:sequence minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1">
<xs:element name="subject_name" type="xs:string" />
<xs:element name="validity" type="Validity" />
<xs:sequence minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:choice minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1">
<xs:element name="allow_rule" minOccurs="0" type="Rule" />
<xs:element name="deny_rule" minOccurs="0" type="Rule" />
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="default" type="DefaultAction" />
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="name" type="xs:string" use="required" />
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="Validity">
<xs:sequence minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1">
<xs:element name="not_before" type="xs:dateTime" />
<xs:element name="not_after" type="xs:dateTime" />
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="Rule">
<xs:sequence minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1">
<xs:element name="domains" type="DomainIdSet" />
<xs:sequence minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element name="publish" type="Criteria" />
</xs:sequence>
<xs:sequence minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element name="subscribe" type="Criteria" />
</xs:sequence>
<xs:sequence minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element name="relay" type="Criteria" />
</xs:sequence>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="DomainIdSet">
<xs:choice minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element name="id" type="DomainId" />
<xs:element name="id_range" type="DomainIdRange" />
</xs:choice>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:simpleType name="DomainId">
<xs:restriction base="xs:nonNegativeInteger" />
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:complexType name="DomainIdRange">
<xs:choice>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="min" type="DomainId" />
<xs:element name="max" type="DomainId" minOccurs="0" />
</xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="max" type="DomainId" />
</xs:choice>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="Criteria">
<xs:all minOccurs="1">
<!-- DDSSEC11-56 -->
<xs:element name="topics" minOccurs="1" type="TopicExpressionList" />
<xs:element name="partitions" minOccurs="0" type="PartitionExpressionList" />
<xs:element name="data_tags" minOccurs="0" type="DataTags" />
</xs:all>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="TopicExpressionList">
<xs:sequence minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element name="topic" type="TopicExpression" />
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="PartitionExpressionList">
<xs:sequence minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element name="partition" type="PartitionExpression" />
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:simpleType name="TopicExpression">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string" />
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="PartitionExpression">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string" />
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:complexType name="DataTags">
<xs:sequence minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element name="tag" type="TagNameValuePair" />
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="TagNameValuePair">
<xs:sequence minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element name="name" type="xs:string" />
<xs:element name="value" type="xs:string" />
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:simpleType name="DefaultAction">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:enumeration value="ALLOW" />
<xs:enumeration value="DENY" />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:schema>这两个文档定义了本地 domain 的权限信息和加密信息,同时也限制了能够接受的远端的 domain 信息。根据 拓展的发现机制 定义的内容,这两个文档本身并不需要传递给对端。
加密
加密插件提供了对数据加密的支持。根据 access control 的配置。加密可以在不同粒度上进行:
| gov | 影响范围 |
|---|---|
TopicRule.data_protection_kind | payload |
TopicRule.metadata_protection_kind | submessage |
DomainRule.rtps_protection_kind | rtps message |
根据 ProtectionKind 的值,加密有三种等级:
| 值 | 加密方式 |
|---|---|
None | 不加密、不签名 |
SIGN | 签名 |
ENCRYPT | 加密 |
| 当 SIGN/ENCRYPT 带有 WITH_ORIGIN_AUTHENTICATION 后缀时。意为将会打开 origin_authenticated 选项。此时,crypto 插件将会为 每对 r/w 生成一个密钥对用来 验证消息来源。 |
加密和认证算法
在加密插件中,DDS 使用 EVP-GCM 进行数据加密和认证。具体原理参见 aes-gcm
| 这里的认证指的是通过对数据签名以验证数据来源,从而达到不可否认的目的。 |
gcm 算法可以简述如下:
C, T = AES-GCM(K, P, AAD, IV)
K:密钥,长度根据算法可为 128bit 或 256bit。
P:plaintext 明文。
AAD: additional authentication data。参与到计算验证信息的过程中。
IV: 初始向量。一般为 96bit。
C: ciphertext 密文。
T: tag 用来解密和验证。为 16bit。
当 P 为空而出现在 AAD 的位置上时,不对数据进行加密,只生成 tag 用来验证。即 GMAC。
根据上述的描述,对于一个 GCM 算法而言,解密需要 K, IV, C, T。因此构造了 KeyMaterial 用来发送 K, IV 信息:
struct KeyMaterial_AES_GCM_GMAC {
CryptoTransformKind transformation_kind;
sequence<octet, 32> master_salt;
CryptoTransformKeyId sender_key_id;
sequence<octet, 32> master_sender_key; (1)
CryptoTransformKeyId receiver_specific_key_id;
sequence<octet, 32> master_receiver_specific_key; (2)
};用来序列化数据
当启用 origin_authenticated 选项时用来为每个 reader 生成认证信息。
对于 DDS-Security 而言,master_sender_key, master_salt 都是随机值,但是对于 BuiltinParticipantVolatileMessageSecureR/W 而言,这两者都是根据 auth 的结果算出来的。
MasterKey := HMACsha256 (sha256(Challenge2 | "key exchange key" | Challenge1) , SharedSecret)
MasterSalt := HMACsha256 (sha256(Challenge1 | "keyexchange salt" | Challenge2) , SharedSecret) (1)Table 67 – KeyMaterial_AES_GCM_GMA
GCM 使用的 key 计算方式如下:
iv := SessionId | InitializationVectorSuffix
key := SessionKey
SessionKey := HMAC256(MasterKey, "SessionKey" | MasterSalt | SessionId)InitializationVectorSuffix 和 SessionId 是一个随机值,会随着消息传递。
基本组件
Crypto 由三个部分构成:
CryptoKeyFactory:负责密钥生成。
CryptoKeyExchange:负责密钥交换。
CryptoPlugin:负责加密和认证。
其结构如下:
密钥生成
security 中的密钥生成是双向的,双方独立生成密钥,并将其发送给对方。
密钥交换
在 R/W 匹配后,双方独立生成自己的密钥,然后通过 DCPSParticipantStatelessMessage 将密钥交换给对方。DCPSParticipantStatelessMessage 的 Payload 由认证过程中得到的密钥进行加密。
数据加密
一块数据被加密后会被组成三个部分:
CryptoHeader:记录了 session_id、iv_suffix 和加密用的 key id。
CryptoContent:密文
CryptoFooter: tag
// Serialized as Big Endian
@extensibility(FINAL)
struct CryptoHeader {
CryptoTransformIdentifier transform_identifier;
octet session_id[4];
octet initialization_vector_suffix[8];
};Footer 储存了 MAC 信息:
// Serialized as Big Endian
@extensibility(FINAL)
struct CryptoFooter {
octet common_mac[16]; (1)
sequence<ReceiverSpecificMAC> receiver_specific_macs; (2)
};aes-gcm 计算出来的 tag。
reader 特定的 mac。
对于 payload 而言,加密后形成下面的内容:
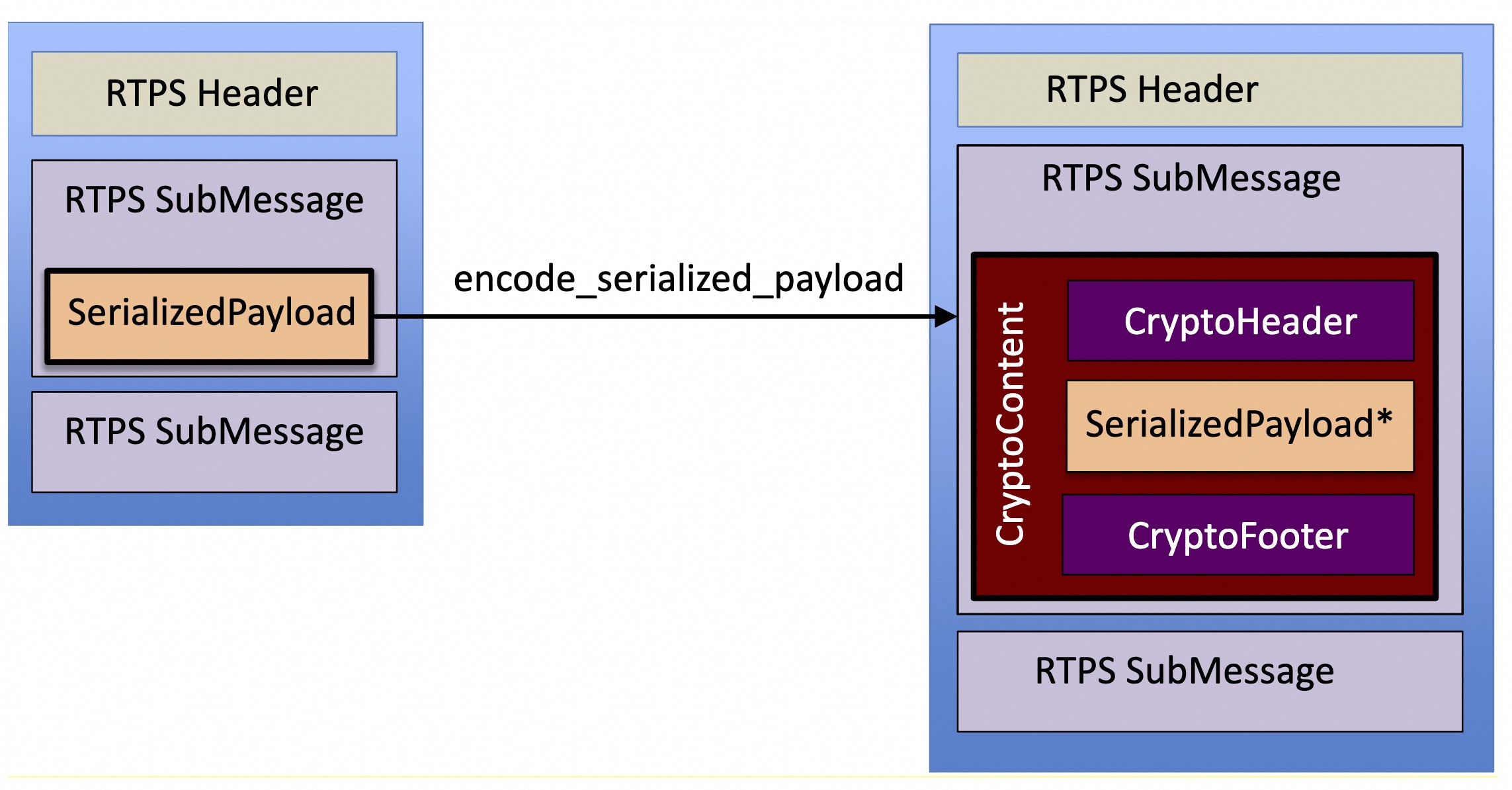
对于 submessage 而言,加密结果如下:
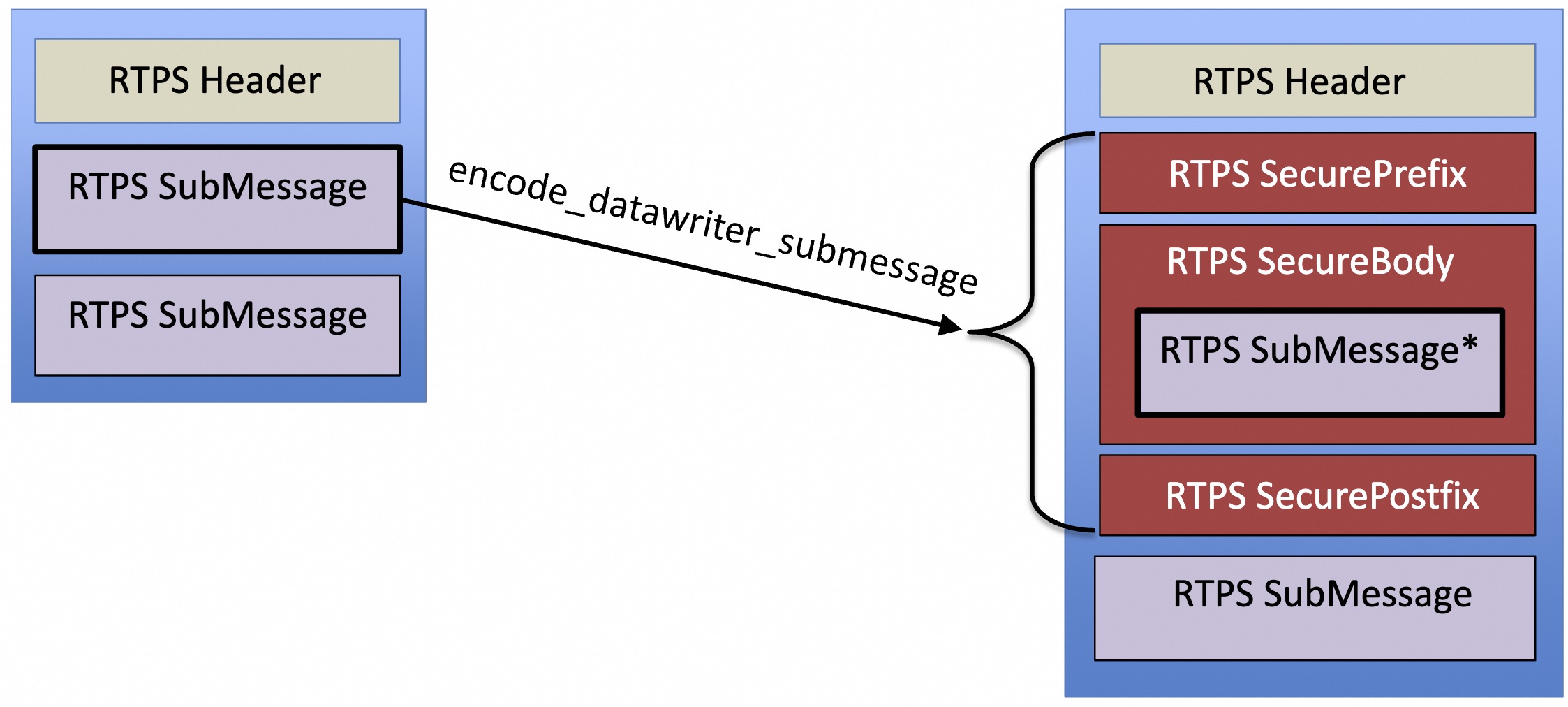
| 加密后一个 submessage 变成了三个 submessage |
对于 rtps message 而言,加密结果如下:
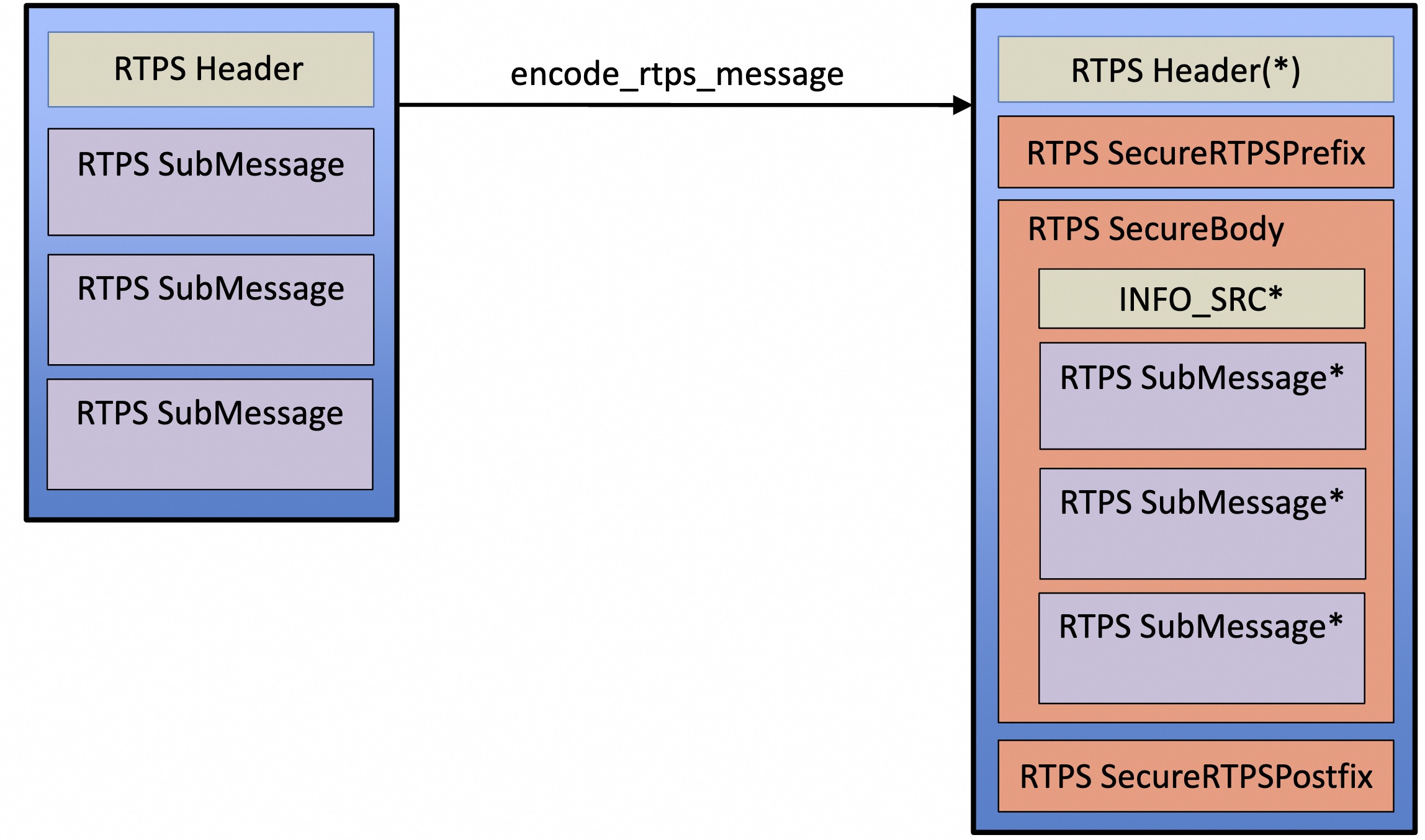
session 管理
session id 是一个 32 位的随机数。session id 具有以下特点:
用来计算 SessionKey。
每次加密都会增加一次 counter。
counter 超过 max_blocks_per_session 后会重新创建 session id。